Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cardiac Biomarkers Phatophysiology
3. Iatrogenic Cardiac Damage Caused by Cancer Treatments
3.1. Cardiotoxicity
3.1.1. Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity
3.1.2. Trastuzumab Cardiotoxcity
3.1.3. Myocarditis Due to Immune Check Points Inhibitors
3.2. Radiotherapy
3.3. Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation/MACEs
3.4. Androgenic Deprivation in Prostate Cancer Patients
4. Cardiac Involvement in Oncological Diseases
4.1. All-Cause Mortality in Newly Diagnosed and Chemotherapy-Naïve Cancer Patients without Evidence of Acute Cardiac Disease
4.2. Carcinoid Heart Disease
4.3. Cardiac AL Amyloidosis
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
- -
- trying to individuate a troponin cut-off that is specific for anthracycline cardiotoxicity, which should have at least a high negative predictive value for future LVD development in order to identify patients who can benefit from a early preventive cardioprotective therapy; in particular, research should focus on that subset of patients with multiple baseline cardiovascular risk factors or who receive high cumulative doses of anthracyclines or who are planned to undergo multiple cardiotoxic treatments in succession (i.e., anthracyclines followed by trastuzumab, anthracyclines followed by mediastinal radiotherapy, etc.), since those are the patients more at risk of developing LVD;
- -
- clearly establishing whether a screening strategy based on serial troponin dosage for ICIs myocarditis is actually useful, taking into account the low incidence of the phenomenon and the frequent cases of isolated aspecific hyper-troponinemia, or if instead it induces only an increase in inappropriate therapy discontinuation rate;
- -
- establishing whether troponin increase during treatment with thoracic radiotherapy correlates with the future development of post-actinic heart disease, although this objective is difficult to achieve given the long interval between therapy end and the eventual development of the disease;
- -
- more quality evidence is needed to establish the utility of NT-proBNP in predicting which patients undergoing androgen deprivation are at risk of developing cardiovascular complications and therefore deserve closer cardiological follow-up and the implementation of preventive cardiac therapy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamorano, J.L.; Lancellotti, P.; Rodriguez Muñoz, D.; Aboyans, V.; Asteggiano, R.; Galderisi, M.; Habib, G.; Lenihan, D.J.; Lip, G.Y.; Lyon, A.R.; et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: The Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 9–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkantaifi, A.; Papadopoulos, C.; Spyropoulou, D.; Toumpourleka, M.; Iliadis, G.; Kardamakis, D.; Nikolaou, M.; Tsoukalas, N.; Kyrgias, G.; Tolia, M. Breast Radiotherapy and Early Adverse Cardiac Effects. The Role of Serum Biomarkers and Strain Echocardiography. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delombaerde, D.; Vervloet, D.; Franssen, C.; Croes, L.; Gremonprez, F.; Prenen, H.; Peeters, M.; Vulsteke, C. Clinical implications of isolated troponinemia following immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.-L.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.-B.; Yan, M.-L.; Xu, Q.-H.; Yan, J. Value of Plasma Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels for Predicting Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmers, D.; Potgieter, D.; Ryan, L.; Fahrner, R.; Rodseth, R.N. The Use of Preoperative B-Type Natriuretic Peptide as a Predictor of Atrial Fibrillation After Thoracic Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Toumpanakis, C.; Caplin, M.E.; Davar, J. Usefulness of N-terminal Pro–Brain Natriuretic Peptide as a Biomarker of the Presence of Carcinoid Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 102, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, M.; Troncone, L.; Del Monte, F. Current and future circulating biomarkers for cardiac amyloidosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, A.S.; Huang, S.J. Cardiac biomarkers in the intensive care unit. Ann. Intensive Care 2012, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rittoo, D.; Jones, A.; Lecky, B.; Neithercut, D. Elevation of cardiac troponin T, but not cardiac troponin I, in patients with neuromuscular diseases: Implications for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2231–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Simoons, M.L.; Chaitman, B.R.; White, H.D.; Katus, H.A.; Apple, F.S.; Lindahl, B.; Morrow, D.A.; et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2551–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passino, C.; Aimo, A.; Masotti, S.; Musetti, V.; Prontera, C.; Emdin, M.; Clerico, A. Cardiac troponins as biomarkers for cardiac disease. Biomark. Med. 2019, 13, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, D.M.; Zaninotto, M.; Cipolla, C.M.; Passino, C.; Plebani, M.; Clerico, A. Cardiotoxic effects and myocardial injury: The search for a more precise definition of drug cardiotoxicity. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 59, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, C.; Wereski, R.; Mills, N.; Chapman, A. Diagnosis, Investigation and Management of Patients with Acute and Chronic Myocardial Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, R.; Masarone, D.; Buono, A.; Gravino, R.; Rea, A.; Salerno, G.; Golia, E.; Ammendola, E.; Del Giorno, G.; Santangelo, L.; et al. Natriuretic peptides: Molecular biology, pathophysiology and clinical implications for the cardiologist. Future Cardiol. 2013, 9, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Madonna, M.; Schiavon, S.; Valenti, V.; Versaci, F.; Zoccai, G.B.; Frati, G.; Sciarretta, S. Cardiovascular Pleiotropic Effects of Natriuretic Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clerico, A.; Zaninotto, M.; Passino, C.; Aspromonte, N.; Piepoli, M.F.; Migliardi, M.; Perrone, M.; Fortunato, A.; Padoan, A.; Testa, A.; et al. Evidence on clinical relevance of cardiovascular risk evaluation in the general population using cardio-specific biomarkers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 59, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, G.C.; Lamantia, G.; Cipolla, C.M.; Cardinale, D. How to identify anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity early and reduce its clinical impact in everyday practice. Kardiol. Pol. 2021, 79, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, G.; Heck, S.L.; Ree, A.H.; Hoffmann, P.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Fagerland, M.W.; Gravdehaug, B.; Von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Bratland, A.; Storås, T.H.; et al. Prevention of cardiac dysfunction during adjuvant breast cancer therapy (PRADA): A 2 × 2 factorial, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of candesartan and metoprolol. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, X.; Rovira, M.; Sitges, M.; Domènech, A.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; de Caralt, T.M.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Perea, R.J.; Monzo, M.; Esteve, J. Enalapril and carvedilol for preventing chemotherapy-induced left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with malignant hemopathies: The OVERCOME trial (preventiOn of left Ventricular dysfunction with Enalapril and caRvedilol in patients submitted to intensive ChemOtherapy for the treatment of Malignant hEmopathies). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinale, D.; Colombo, A.; Sandri, M.T.; Lamantia, G.; Colombo, N.; Civelli, M.; Martinelli, G.; Veglia, F.; Fiorentini, C.; Cipolla, C.M.; et al. Prevention of High-Dose Chemotherapy–Induced Cardiotoxicity in High-Risk Patients by Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition. Circulation 2006, 114, 2474–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinale, D.; Ciceri, F.; Latini, R.; Franzosi, M.G.; Sandri, M.T.; Civelli, M.; Cucchi, G.; Menatti, E.; Mangiavacchi, M.; Cavina, R.; et al. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: A multicenter randomised trial comparing two strategies for guiding prevention with enalapril: The International CardioOncology Society-one trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 94, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerico, A.; Zaninotto, M.; Passino, C.; Padoan, A.; Migliardi, M.; Plebani, M. High-sensitivity methods for cardiac troponins: The mission is not over yet. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 103, 215–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerico, A.; Ripoli, A.; Zaninotto, M.; Masotti, S.; Musetti, V.; Ciaccio, M.; Aloe, R.; Rizzardi, S.; Dittadi, R.; Carrozza, C.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of plasma cTnI concentration values measured with three high-sensitivity methods in a large Italian population of healthy volunteers and patients admitted to emergency department with acute coronary syndrome: A multi-center study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 496, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerico, A.; Zaninotto, M.; Ripoli, A.; Masotti, S.; Prontera, C.; Passino, C.; Plebani, M. The 99th percentile of reference population for cTnI and cTnT assay: Methodology, pathophysiology and clinical implications. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerico, A.; Giannoni, A.; Prontera, C.; Giovannini, S. High-sensitivity troponin: A new tool for pathophysiological investigation and clinical practice. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2009, 49, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, R.; Silva, L.M.; Cruz, A.L.V.M.; Fraga, V.G.; Sabino, A.D.P.; Gomes, K.B. Troponin as a cardiotoxicity marker in breast cancer patients receiving anthracycline-based chemotherapy: A narrative review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, F.-M.; Genser, N.; Fink, C.; Falk, M.; Mair, J.; Maurer-Dengg, K.; Hammerer, I.; Puschendorf, B. Cardiac troponin T and creatine kinase MB mass concentrations in children receiving anthracycline chemotherapy. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1995, 25, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, E.H.; Lipshultz, S.E.; Rifai, N.; Zhang, J.; Papoian, T.; Yu, Z.X.; Takeda, K.; Ferrans, V.J. Use of cardiac troponin T levels as an indicator of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, E.H.; Zhang, J.; Lipshultz, S.E.; Rifai, N.; Chadwick, D.; Takeda, K.; Yu, Z.-X.; Ferrans, V.J. Correlation Between Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponin-T and the Severity of the Chronic Cardiomyopathy Induced by Doxorubicin. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, E.H.; Zhang, J.; Rifai, N.; Lipshultz, S.E.; Hasinoff, B.B.; Chadwick, D.P.; Knapton, A.; Chai, J.; Ferrans, V.J. The use of serum levels of cardiac troponin T to compare the protective activity of dexrazoxane against doxorubicin- and mitoxantrone-induced cardiotoxicity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2001, 48, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparano, J.A.; Brown, D.L.; Wolff, A.C. Predicting Cancer Therapy—Induced Cardiotoxicity. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, D.; Sandri, M.T.; Martinoni, A.; LabTech, A.T.; Civelli, M.; Lamantia, G.; Cinieri, S.; Martinelli, G.; Cipolla, C.M.; Fiorentini, C. Left ventricular dysfunction predicted by early troponin I release after high-dose chemotherapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, M.; Kervancioglu, M. Plasma concentrations of NT-pro-BNP and cardiac troponin-I in relation to doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and cardiac function in childhood malignancy. Saudi Med. J. 2005, 26, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Kısmet, E.; Varan, A.; Ayabakan, C.; Alehan, D.; Portakal, O.; Büyükpamukçu, M. Serum troponin T levels and echocardiographic evaluation in children treated with doxorubicin. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2003, 42, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feola, M.; Garrone, O.; Occelli, M.; Francini, A.; Biggi, A.; Visconti, G.; Albrile, F.; Bobbio, M.; Merlano, M. Cardiotoxicity after anthracycline chemotherapy in breast carcinoma: Effects on left ventricular ejection fraction, troponin I and brain natriuretic peptide. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 148, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witteles, R.M. Biomarkers as Predictors of Cardiac Toxicity from Targeted Cancer Therapies. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatici, M.; Cardinale, D.; Botteri, E.; Bagnardi, V.; Mauro, C.; Cassatella, M.C.; Lentati, F.B.; Zorzino, L.; Passerini, R. TnI-Ultra assay measurements in cancer patients: Comparison with the conventional assay and clinical implication. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2014, 74, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Mincu, R.I.; Mahabadi, A.A.; Settelmeier, S.; Al-Rashid, F.; Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M. Troponins and brain natriuretic peptides for the prediction of cardiotoxicity in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart. Fail. 2020, 22, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, L.; Mincu, R.I.; Mrotzek, S.M.; Korste, S.; Neudorf, U.; Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M. Cardiac biomarkers for the detection of cardiotoxicity in childhood cancer—A meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, L.; Sun, M.; Chen, H.; Pan, C.; Shu, X. Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography combined with high-sensitive cardiac troponin T in early detection and prediction of cardiotoxicity during epirubicine-based chemotherapy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzolos, E.; Adamson, P.; Hall, P.; Macpherson, I.; Oikonomidou, O.; MacLean, M.; Lewis, S.; McVicars, H.; Newby, D.; Mills, N.; et al. Dynamic Changes in High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I in Response to Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinale, D.; Colombo, A.; Torrisi, R.; Sandri, M.T.; Civelli, M.; Salvatici, M.; Lamantia, G.; Colombo, N.; Cortinovis, S.; Dessanai, M.A.; et al. Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Clinical and Prognostic Implications of Troponin I Evaluation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3910–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewer, M.S.; Ewer, S.M. Troponin I Provides Insight into Cardiotoxicity and the Anthracycline-Trastuzumab Interaction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3901–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhesy-Thind, S.; Ellis, P.M.; Mukherjee, S.D.; Mackett, K.; Bordeleau, L.; Kavsak, P.A. Longitudinal High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Measurements in Patients with Breast Cancer Receiving Trastuzumab. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 545.e1–545.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zardavas, D.; Suter, T.M.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.D.; Steinseifer, J.; Noe, J.J.; Lauer, S.S.; Al-Sakaff, N.N.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; de Azambuja, E. Role of Troponins I and T and N-Terminal Prohormone of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in Monitoring Cardiac Safety of Patients with Early-Stage Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive Breast Cancer Receiving Trastuzumab: A Herceptin Adjuvant Study Cardiac Marker Substudy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponde, N.; Bradbury, I.; Lambertini, M.; Ewer, M.; Campbell, C.; Ameels, H.; Zardavas, D.; Di Cosimo, S.; Baselga, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Cardiac biomarkers for early detection and prediction of trastuzumab and/or lapatinib-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer: A NeoALTTO sub-study (BIG 1-06). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 168, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Fradley, M.G.; Cohen, J.V.; Nohria, A.; Reynolds, K.L.; Heinzerling, L.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Damrongwatanasuk, R.; Chen, C.L.; Gupta, D.; et al. Myocarditis in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, H.; Alhussein, M.M.; Alrashidi, S.; Alzayer, H.; Alshatti, A.; Valettas, N.; Mukherjee, S.D.; Nair, V.; Leong, D.P. Cardiac Complications Associated with Checkpoint Inhibition: A Systematic Review of the Literature in an Important Emerging Area. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.J.; Spehlmann, M.E.; Frey, N. Cardio-toxicity of checkpoint inhibitors. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10 (Suppl. 35), S4400–S4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Y.; Okoye, G.; Neilan, T.G.; Johnson, D.B.; Moslehi, J.J. Cardiovascular Toxicities Associated with Cancer Immunotherapies. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2017, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spallarossa, P.; Tini, G.; Sarocchi, M.; Arboscello, E.; Grossi, F.; Queirolo, P.; Zoppoli, G.; Ameri, P. Identification and Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Related Myocarditis: Use Troponin Wisely. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2201–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spallarossa, P.; Sarocchi, M.; Tini, G.; Arboscello, E.; Toma, M.; Ameri, P.; Porto, I. How to Monitor Cardiac Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarocchi, M.; Grossi, F.; Arboscello, E.; Bellodi, A.; Genova, C.; Bello, M.G.D.; Rijavec, E.; Barletta, G.; Biello, F.; Ghigliotti, G.; et al. Serial Troponin for Early Detection of Nivolumab Cardiotoxicity in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. The Oncologist 2018, 23, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waliany, S.; Neal, J.W.; Reddy, S.; Wakelee, H.; Shah, S.A.; Srinivas, S.; Padda, S.K.; Fan, A.C.; Colevas, A.D.; Wu, S.M.; et al. Myocarditis Surveillance With High-Sensitivity Troponin I During Cancer Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławiński, G.; Wrona, A.; Dąbrowska-Kugacka, A.; Raczak, G.; Lewicka, E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cardiac Toxicity in Patients Treated for Non-Small Lung Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Lacchetti, C.; Schneider, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Gardner, J.M.; Ginex, P.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1714–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes-Davies, L.; Sacks, D.; Rescigno, J.; Howard, S.; Harris, J. Serum cardiac troponin T levels during treatment of early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 2582–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellessen, U.; Zingel, M.; Hecker, H.; Bahnsen, J.; Borschke, D. Effects of Radiation Therapy on Myocardial Cell Integrity and Pump Function: Which Role for Cardiac Biomarkers? Chemotherapy 2010, 56, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, E.; Fahmy, E.; Mahmoud, K.; El Kerm, Y.; Auf, M. Assessment of the onset of radiation-induced cardiac damage after radiotherapy of breast cancer patients. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyttä, T.; Tuohinen, S.S.; Boman, E.; Virtanen, V.; Raatikainen, P.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L. Troponin T-release associates with cardiac radiation doses during adjuvant left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skyttä, T.; Tuohinen, S.; Luukkaala, T.; Virtanen, V.; Raatikainen, P.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L. Adjuvant radiotherapy-induced cardiac changes among patients with early breast cancer: A three-year follow-up study. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, E.; Dhesy-Thind, S.; Swaminath, A.; Leong, D.; Pond, G.; Voruganti, S.; Sussman, J.; Wright, J.; Okawara, G.; Kavsak, P.; et al. MEDiastinal Irradiation and CArdio-Toxic Effects (MEDICATE): Exploring the Relationship between Cardiac Irradiation and High Sensitivity Troponins. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Alfò, M.; Vitiello, C.; Vullo, G.; Facondo, G.; Marinelli, L.; Burocchi, S.; Gallo, G.; Valeriani, M.; Campanella, B.; et al. Markers of Cardiotoxicity in Early Breast Cancer Patients Treated with a Hypofractionated Schedule: A Prospective Study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, e141–e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.F.; Ho, A.Y.; Braunstein, L.Z.; Thor, M.E.; Chuy, K.L.; Eaton, A.; Mara, E.; Cahlon, O.; Dang, C.T.; Oeffinger, K.C.; et al. Assessment of Early Radiation-Induced Changes in Left Ventricular Function by Myocardial Strain Imaging After Breast Radiation Therapy. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibene, T.; Michieletto, S.; Evangelista, L.; Bianchi, A.; Orvieto, E.; Lora, O.; Berti, F.; Bozza, F.; Banzato, A. Intraoperative radiotherapy during breast cancer surgery: Acute and chronic cardiac safety tested by an ultra-sensitive troponin and N-terminal Pro-B-type natriuretic peptide. Eur. J. Oncol. 2014, 19, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic, S.; Berlit, S.; Sperk, E.; Wenz, F.; Weiß, C.; Trinkmann, F.; Sütterlin, M.; Tuschy, B. Cardiac serum marker alterations after intraoperative radiotherapy with low-energy x-rays in early breast cancer as an indicator of possible cardiac toxicity. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudil, R.; Mueller, C.; Čelutkienė, J.; Henriksen, P.A.; Lenihan, D.; Dent, S.; Barac, A.; Stanway, S.; Moslehi, J.; Suter, T.M.; et al. Role of serum biomarkers in cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic cancer therapies: A position statement from the Cardio-Oncology Study Group of the Heart Failure Association and the Cardio-Oncology Council of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1966–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, D.; Colombo, A.; Sandri, M.T.; Lamantia, G.; Colombo, N.; Civelli, M.; Salvatici, M.; Veronesi, G.; Veglia, F.; Fiorentini, C.; et al. Increased Perioperative N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Levels Predict Atrial Fibrillation After Thoracic Surgery for Lung Cancer. Circulation 2007, 115, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, T.; Maeda, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Funakoshi, Y.; Kimura, T.; Maekura, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Okumura, M. Predictive value of B-type natriuretic peptide for postoperative atrial fibrillation following pulmonary resection for lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2010, 37, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Wu, J.; Simon, C.; Barlera, S.; Marchioli, R.; Mariani, J.; Macchia, A.; Lombardi, F.; Vago, T.; Aleksova, A.; et al. Circulating cardiac biomarkers and postoperative atrial fibrillation in the OPERA trial. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Romero, D.; Vílchez, J.A.; Lahoz, A.; Romero-Aniorte, A.I.; Orenes-Piñero, E.; Caballero, L.; Jara-Rubio, R.; Arribas, J.M.; García-Alberola, A.; Valdés, M.; et al. High-sensitivity troponin T as a biomarker for the development of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2014, 45, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knayzer, B.; Abramov, D.; Natalia, B.; Tovbin, D.; Ganiel, A.; Katz, A. Atrial Fibrillation and Plasma Troponin I Elevation After Cardiac Surgery: Relation to Inflammation-Associated Parameters. J. Card. Surg. 2007, 22, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, J.C.; Petrucci, O.; Godoy, M.F.; Braile, D.M. Perioperative serum troponin I levels are associated with higher risk for atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. 2012, 14, 22–25. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahoz-Tornos, Á.; Vilchez-Aguilera, J.A.; Hernandez-Romero, D.; Romero-Aniorte, A.I.; Orenes-Piñero, E.; Jara-Rubio, R.; Del Saz-Ortiz, A.; Arribas-Leal, J.M.; García-Alberola, A.; Valdés-Chávarri, M.; et al. Colesterol HDL y troponina T ultrasensible como biomarcadores predictivos de fibrilación auricular postoperatoria [HDL cholesterol and high-sensitive troponin T as predictive biomarkers of atrial fibrillation after heart surgery]. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2015, 85, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Uchoa, R.B.; Caramelli, B. Troponin I as a mortality marker after lung resection surgery—A prospective cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margel, D.; Peer, A.; Ber, Y.; Shavit-Grievink, L.; Tabachnik, T.; Sela, S.; Witberg, G.; Baniel, J.; Kedar, D.; Duivenvoorden, W.C.M.; et al. Cardiovascular Morbidity in a Randomized Trial Comparing GnRH Agonist and GnRH Antagonist among Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer and Preexisting Cardiovascular Disease. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, S.; Campazzi, E.; Zanardi, S.; Puntoni, M.; Piccininno, M.; Piccardo, A.; Naseri, M.S.Z.; Defferrari, C.; Provinciali, N.; Petrera, M.; et al. Association of Biomarkers with Serious Cardiac Adverse Events during Abiraterone Acetate Treatment in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margel, D.; Ber, Y.; Peer, A.; Shavit-Grievink, L.; Pinthus, J.H.; Witberg, G.; Baniel, J.; Kedar, D.; Rosenbaum, E. Cardiac biomarkers in patients with prostate cancer and cardiovascular disease receiving gonadotrophin releasing hormone agonist vs antagonist. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloni, C.; Slovin, S.F.; Blemings, A.; Goodman, S.G.; Evans, C.P.; Nilsson, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Zubovskiy, K.; Olesen, T.K.; Dugi, K.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Degarelix Versus Leuprolide for Advanced Prostate Cancer. CardioOncol. 2020, 2, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.; Thompson, E.W.; Demissei, B.; Ho, J.E.; Januzzi, J.L.; Ky, B. Mechanistic Biomarkers Informative of Both Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavo, N.; Raderer, M.; Hülsmann, M.; Neuhold, S.; Adlbrecht, C.; Strunk, G.; Goliasch, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Steger, G.G.; Hejna, M.; et al. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cancer and their association with all-cause mortality. Heart 2015, 101, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, D.; Romann, S.W.; Heckmann, M.B.; Hund, H.; Bougatf, N.; Kantharajah, A.; Katus, H.A.; Müller, O.J.; Frey, N.; Giannitsis, E.; et al. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T determines all-cause mortality in cancer patients: A single-centre cohort study. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovani, M.; Liu, E.; Paniagua, S.M.; Lau, E.S.; Li, S.X.; Takvorian, K.S.; Kreger, B.E.; Splansky, G.L.; de Boer, A.R.; Joshi, A.D.; et al. Cardiovascular disease related circulating biomarkers and cancer incidence and mortality: Is there an association? Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, cvab282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, W.G.; Swaanenburg, J.C.; Van Veldhuisen, D.; Kema, I.P.; Willemse, P.H.; de Vries, E. Troponin I, Troponin T, and Creatine Kinase-MB Mass in Patients with the Carcinoid Syndrome with and without Heart Failure. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 2296–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuetenhorst, J.M.; Korse, C.M.; Bonfrer, J.M.G.; Bakker, R.H.; Taal, B.G. Role of natriuretic peptides in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with carcinoid heart disease. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korse, C.M.; Taal, B.G.; de Groot, C.A.; Bakker, R.H.; Bonfrer, J.M. Chromogranin-A and N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide: An Excellent Pair of Biomarkers for Diagnostics in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Burgess, M.I.; Banks, M.; Pritchard, D.M.; Vora, J.; Valle, J.; Wong, C.; Chadwick, C.; George, K.; Keevil, B.; et al. The Association of a Panel of Biomarkers with the Presence and Severity of Carcinoid Heart Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davar, J.; Connolly, H.M.; Caplin, M.E.; Pavel, M.; Zacks, J.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Cuthbertson, D.; Dobson, R.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Steeds, R.; et al. Diagnosing and Managing Carcinoid Heart Disease in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1288–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Wright, R.; McGregor, C.G.; Dispenzieri, A.; McConnell, J.P.; Burritt, M.F.; Jaffe, A.S. Troponin levels in patients with amyloid cardiomyopathy undergoing cardiac transplantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, A.R.; Gertz, A.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Miller, W.L.; Chandrasekaran, K.; McConnell, J.P.; Burritt, M.F.; Jaffe, A.S. Survival in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis and raised serum cardiac troponins. Lancet 2003, 361, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Campana, C.; Klersy, C.; Balduini, A.; Vadacca, G.; Perfetti, V.; Perlini, S.; Obici, L.; Ascari, E.; D’Eril, G.M.; et al. Serum N-Terminal Pro–Brain Natriuretic Peptide Is a Sensitive Marker of Myocardial Dysfunction in AL Amyloidosis. Circulation 2003, 107, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Burritt, M.F.; Therneau, T.M.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; et al. Serum Cardiac Troponins and N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide: A Staging System for Primary Systemic Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Burritt, M.F.; Therneau, T.M.; McConnell, J.P.; Litzow, M.R.; Gastineau, D.A.; Tefferi, A.; et al. Prognostication of survival using cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004, 104, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellavia, D.; Pellikka, P.A.; Al-Zahrani, G.B.; Abraham, T.P.; Dispenzieri, A.; Miyazaki, C.; Lacy, M.; Scott, C.; Oh, J.K.; Miller, F.A. Independent Predictors of Survival in Primary Systemic (AL) Amyloidosis, Including Cardiac Biomarkers and Left Ventricular Strain Imaging: An Observational Cohort Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellavia, D.; Pellikka, P.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Scott, C.G.; Al-Zahrani, G.B.; Grogan, M.; Pitrolo, F.; Oh, J.K.; Miller, F.A. Comparison of right ventricular longitudinal strain imaging, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and cardiac biomarkers for early diagnosis of cardiac involvement and risk stratification in primary systematic (AL) amyloidosis: A 5-year cohort study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palladini, G.; Barassi, A.; Klersy, C.; Pacciolla, R.; Milani, P.; Sarais, G.; Perlini, S.; Albertini, R.; Russo, P.; Foli, A.; et al. The combination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) at presentation and changes in N-terminal natriuretic peptide type B (NT-proBNP) after chemotherapy best predicts survival in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010, 116, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apridonidze, T.; Steingart, R.M.; Comenzo, R.L.; Hoffman, J.; Goldsmith, Y.; Bella, J.N.; Landau, H.; Liu, J.E. Clinical and Echocardiographic Correlates of Elevated Troponin in Amyloid Light-Chain Cardiac Amyloidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Colby, C.; Laumann, K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Leung, N.; Dingli, D.; et al. Revised Prognostic Staging System for Light Chain Amyloidosis Incorporating Cardiac Biomarkers and Serum Free Light Chain Measurements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, A.M.; Kumar, S.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Kyle, A.R.; Saenger, A.K.; Grogan, M.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.; et al. High sensitivity cardiac troponin T in patients with immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Heart 2014, 100, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

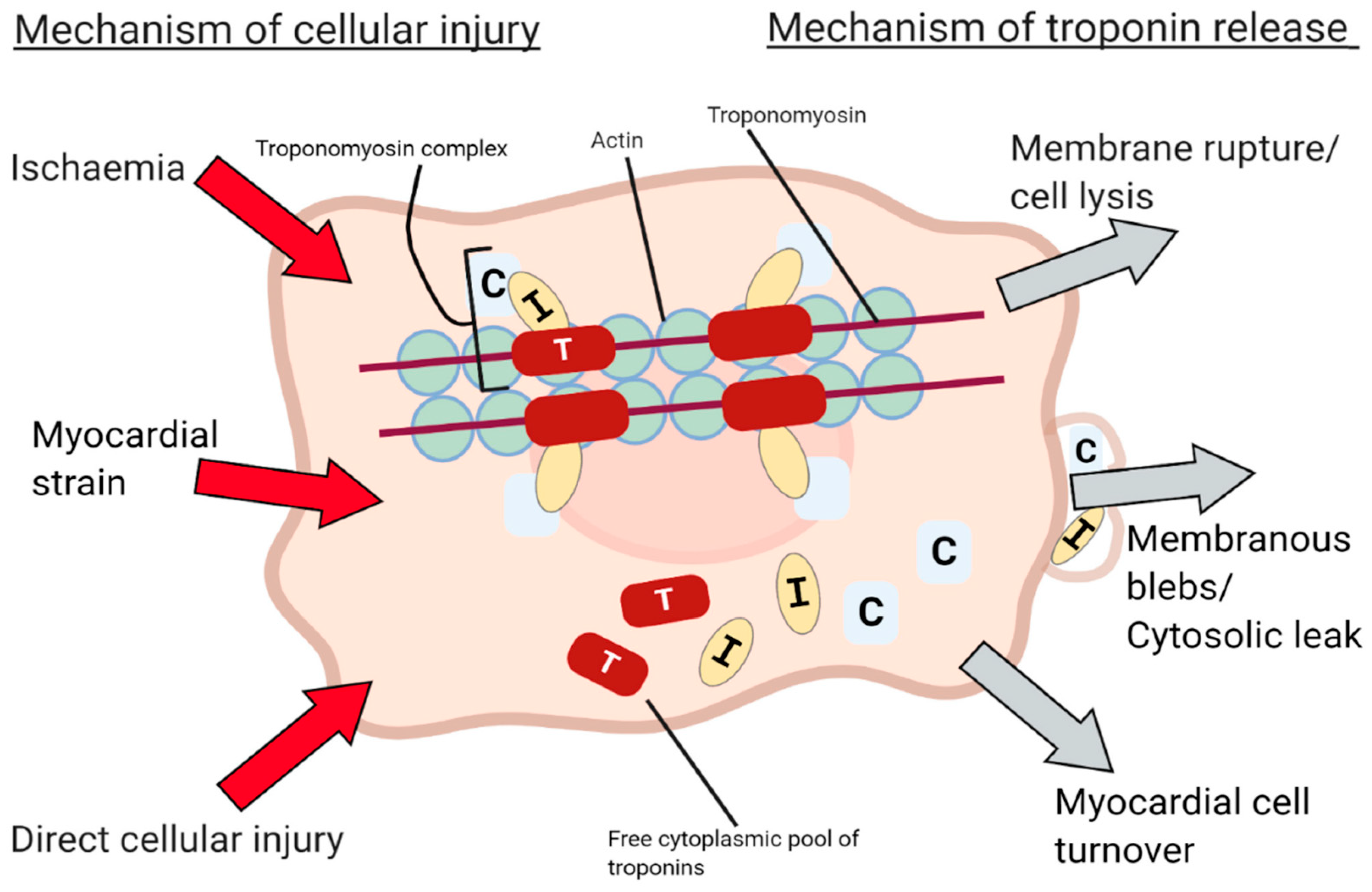
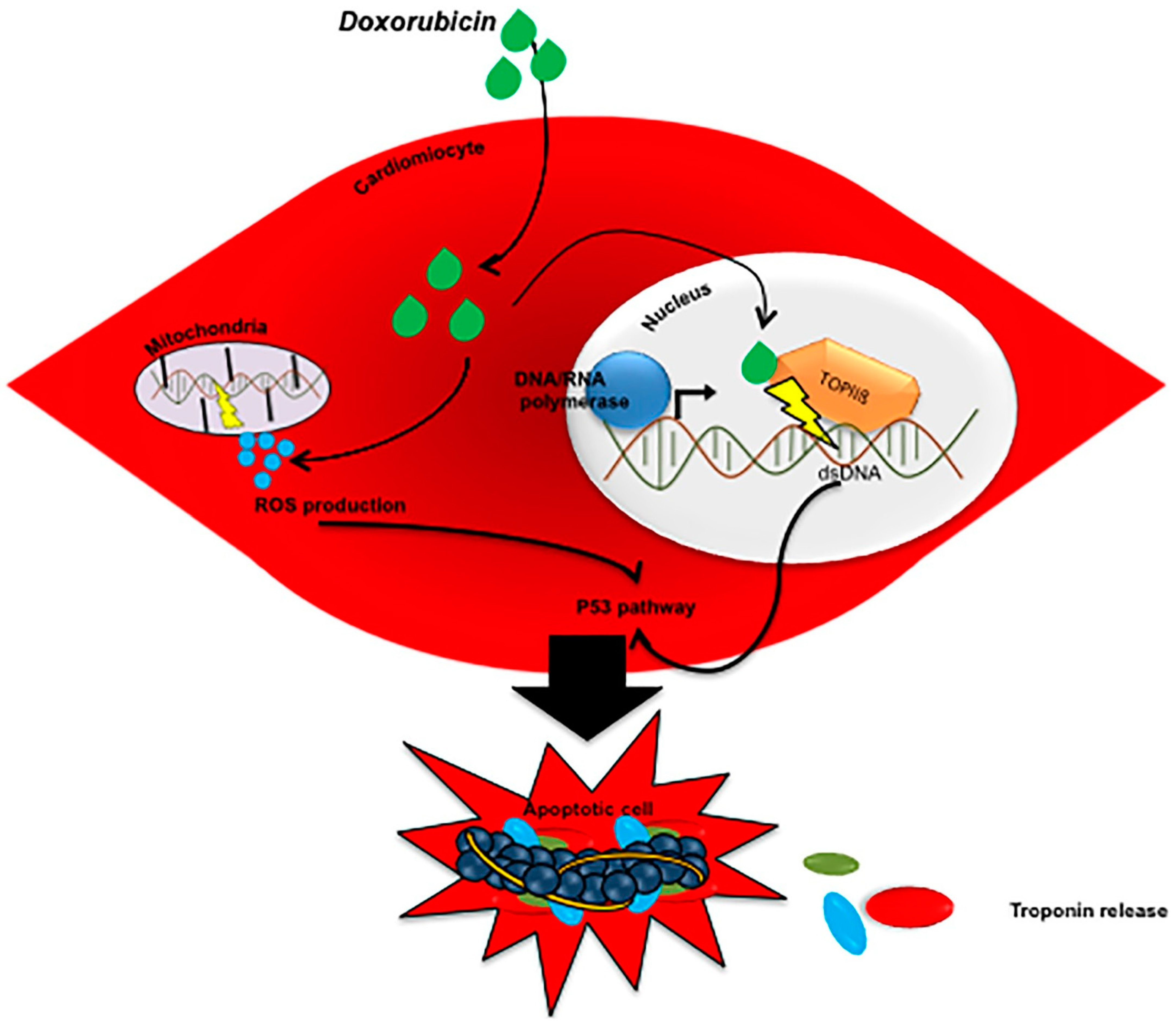


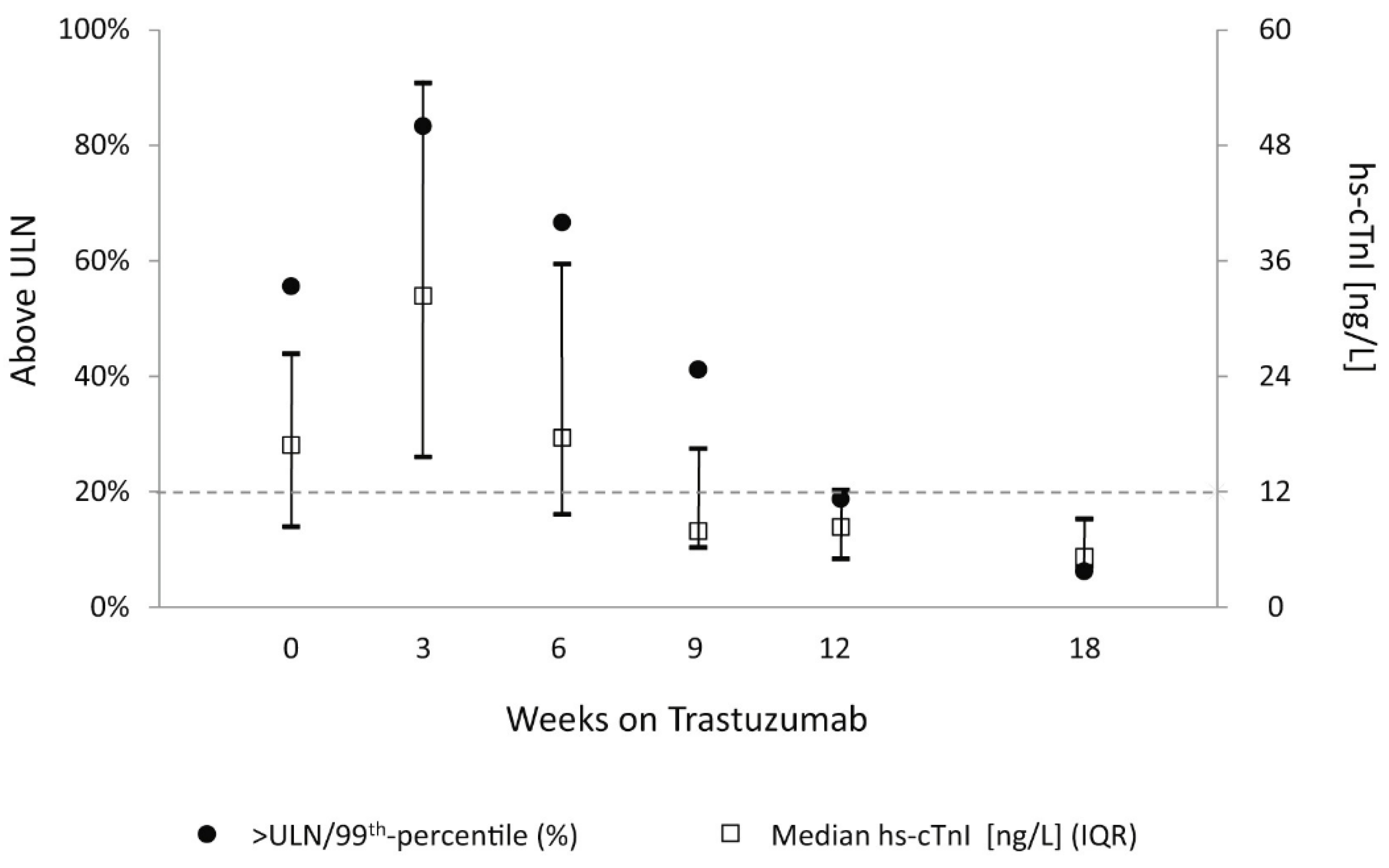






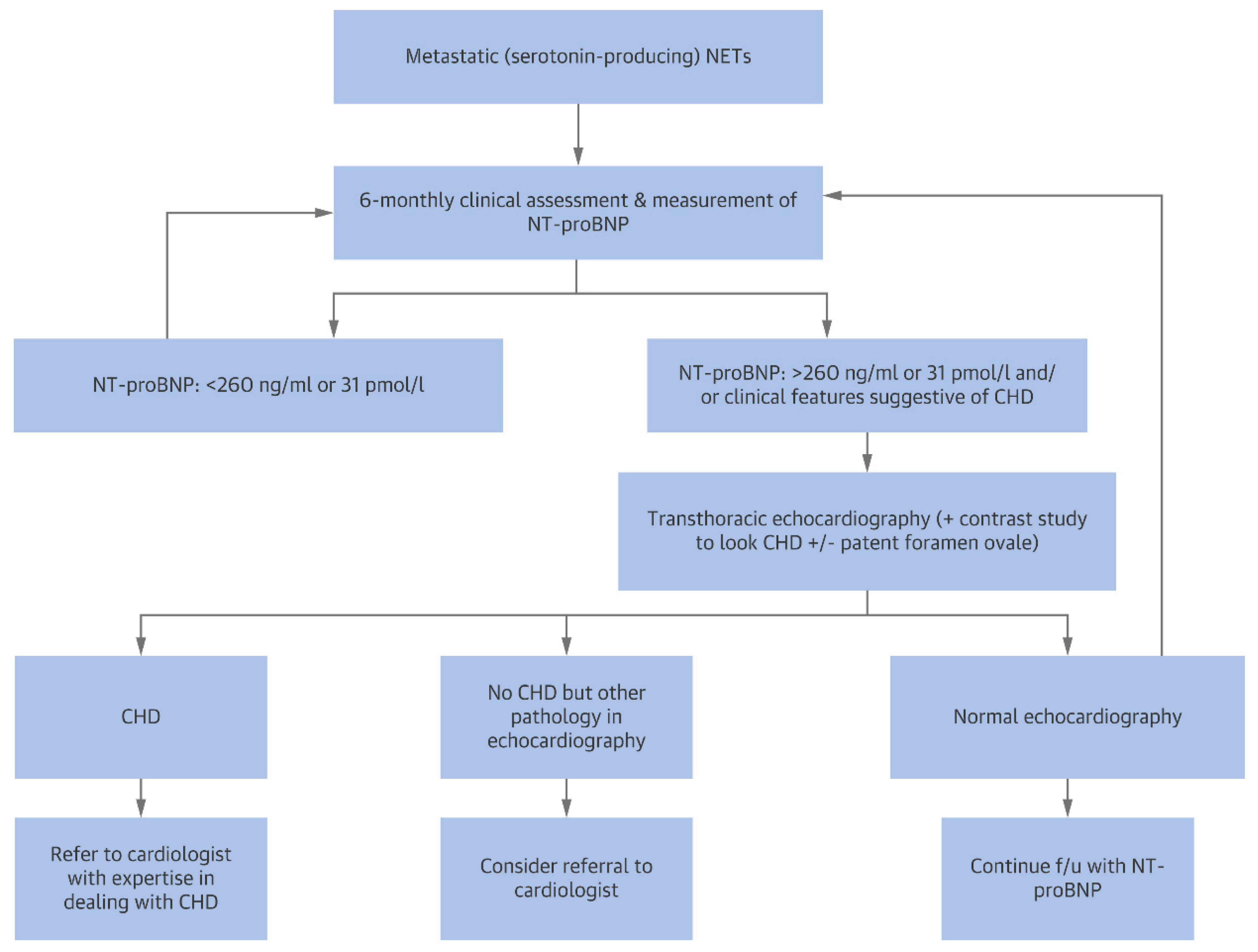
| Main Phatophysiological Mechanism | Pathology |
|---|---|
| Injury related to primary myocardial ischemia | Plaque rupture |
| Intraluminal coronary artery thrombus formation | |
| Injury related to supply/demand imbalance of myocardial ischemia | Tachy-/brady-arrhythmias |
| Aortic dissection or severe aortic valve disease | |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | |
| Cardiogenic, hypovolemic, or septic shock | |
| Severe respiratory failure | |
| Severe anemia | |
| Hypertension with or without LVH | |
| Coronary spasm | |
| Coronary embolism or vasculitis | |
| Coronary endothelial dysfunction without significant CAD | |
| Injury not related to myocardial ischemia | Cardiac contusion, surgery, ablation, pacing, or defibrillator shocks |
| Rhabdomyolysis with cardiac involvement | |
| Myocarditis | |
| Cardiotoxic agents, e.g., anthracyclines, herceptin | |
| Multifactorial or indeterminate myocardial injury | Heart failure |
| Stress (Takotsubo) cardiomyopathy | |
| Severe pulmonary embolism or pulmonary hypertension | |
| Sepsis and critically ill patients | |
| Renal failure | |
| Severe acute neurological diseases, e.g., stroke, subarachnoid | |
| hemorrhage | |
| Infiltrative diseases, e.g., amyloidosis, sarcoidosis | |
| Strenuous exercise |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semeraro, G.C.; Cipolla, C.M.; Cardinale, D.M. Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215426
Semeraro GC, Cipolla CM, Cardinale DM. Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215426
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemeraro, Gennaro Carmine, Carlo Maria Cipolla, and Daniela Maria Cardinale. 2021. "Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215426
APA StyleSemeraro, G. C., Cipolla, C. M., & Cardinale, D. M. (2021). Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients. Cancers, 13(21), 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215426






